Health supplement is often used as an alternative to supplement the diet and to maintain, enhance, and improve the health status and function of the human body. It might contain one or more active ingredients such as vitamins, minerals, amino acids, enzymes, herbs, or other pharmaceutical ingredients.

Health supplement is not only available in tablets or capsules form, it can be presented in various forms such as softgel, powder, gummies, and liquid. Even though a health supplement is not a drug or medicine, but they have similarities with medicines, where people should follow the recommended dosage as it might cause a negative impact on health with overdose.
The recommended serving size or dosage of the health supplement is provided and labeled on the product, but for people with certain health conditions should consult a doctor or healthcare provider before consumption. Also, recommended dosage might be different based on the person’s health status, and the efficacy of health supplement might be affected by several factors, such as alcohol consumption, caffeine intake, stress, medications and prescription drugs, antibiotics, and gastrointestinal disorder.

Alcohol consumption
Alcohol consumption is always associated with increased risk of chronic diseases. Alcohol interferes the nutrient absorption by affecting the digestion, storage, utilization, and excretion of nutrients.
- Alcohol causes decreased secretion of digestive enzymes, which then inhibit the breakdown of nutrients into usable molecules.
- Alcohol could damage the cell lining the stomach and intestine, disabling the transport of some nutrients into the blood.
- Alcohol causes impaired digestion of proteins, impaired processing of amino acid by small intestine and liver, impaired synthesis of protein from amino acids.
- Alcohol inhibits fat absorption, impaired absorption of vitamins A, D, E, and K that are normally absorbed along with dietary fats.
The recommended intake of alcohol for men is 2 drinks per day while for women is 1 drink per day based on the Dietary Guideline for Americans. The size of a drink is 12 oz of 5% alc. beer, or 8 oz of 7% alc. malt liquor, or 5 oz of 12% alc. wine, or 1.5 oz of 40% alc. liquor.

High caffeine intake
Researchers suggested moderate caffeine intake which is not more than 300 mg per day (less than 3 cups of coffee) might not cause any negative effect on the body health, but over-consumption of caffeinated beverages which is more than 350 mg per day for long term might interfere with nutrients absorption and causes nutrient depletion.
- Caffeine has a mild diuretic effect which increases urination. Increase urination causes loss of water-soluble nutrients, such as B-vitamins and vitamin C.
- Caffeine interferes absorption of minerals, such as calcium, iron, and magnesium.
- Caffeine increases the risk of osteoporosis by inhibiting vitamin D receptors, interfere with the absorption and use of calcium in building bone, calcium excreted in the urine, and decrease bone mineral density.
- Caffeine might reduce the absorption of manganese, zinc, and copper, increase the excretion of magnesium, potassium, sodium, and phosphate.
Coffee is one of the caffeine-rich beverages, however, tea, chocolate, and energy drinks also contained caffeine. Normally, 8 oz of drip-brewed coffee contains 65-120 mg of caffeine. Consumption of health supplements should be separated at least one hour after consumed caffeinated beverages.

Stress
Under a stressful condition, the body will activate the “flight or fight” response, in which the body can prioritize more important functions such as heart and breathing rate to prepare the body for attack or escape. This response will affect digestion by restricting blood flow, slowing the contractions of digestive muscle, and decreasing secretions needed for digestion.
- Stress can affect brain-gut communication, might weaken gastric secretion, cause gut discomfort such as bloating, nausea, and increase the severity of heartburn.
- Stress can affect bowel movement, which is how quickly the food move through the body, causes either diarrhea or constipation, and reduce the absorption of nutrients in the intestine.
- Stress can affect the microbiota in the intestine, weaken the intestinal barrier and allow gut bacteria to enter the body, and lead to inflammation.
Medications and prescription drugs
Consumption of certain medications and prescription drugs with food or health supplement might cause drug-nutrient interaction, which will alter the efficacy of medications, or interfere with nutrients absorption and affect the nutritional status of the body.
- Anti-inflammatory drug, such as acetylsalicylic acid, when it was taken close to or during meals, might deplete absorption of vitamin C and K, also increase excretion of thiamine, folic acid, and amino acids.
- Laxative drug, such as mineral oil might deplete the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K.
- Fiber supplements may cause the other medications to become less effective if given at the same time.
All oral medications should be administered at least 2 hours before or 2 hours after dosing of health supplements.
However, some medications require administration with meals to increase the absorption of medicines, reduce the irritating effect of medicines on the gastrointestinal tract, and help in treatment compliance. Hence, it is best to consult doctors or health professional before taking any health supplements and medicines.

Antibiotic
Antibiotic is an anti-infective agent, which is used to fight against bacterial infection. However, it is not only inhibiting activities of harmful bacteria, it might also affect gut microbiota in the intestine, such as interfere with gut motility, influence nutrients absorption, and some might negatively impact nutritional status and gut health.
- Penicillin is antibiotic with an excellent safety profile with few exceptions to allergy, but a high and long-term dose of penicillin might disturb digestion and eliminate healthy gut bacteria.
- Amikacin is an antibiotic that fights against gram-negative bacteria, but it might reduce calcium absorption, and decrease the level of vitamins by altering the intestinal absorption.
- Neomycin used in suppressing the intestinal bacteria can cause malabsorption of glucose, sodium, calcium, vitamin B12, and iron.
Antibiotics are specific for the types of bacteria being treated. It is important not to use an antibiotic without a prescription from a doctor, even if it’s in the same drug you were previously prescribed. Also, a full treatment regimen is necessary to effectively cure the infection, so don’t use or give away leftover antibiotics.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Gastrointestinal disorders might cause malabsorption which impaired nutrients absorption and impact nutritional status in the body.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) such as Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis which might cause intestine mucosal injury and lost intestinal absorptive surface area, leading to fat and carbohydrate malabsorption.
- Chronic pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis which cause impaired pancreatic enzyme activity might lead to protein malabsorption.
- Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) which causes bile acid ineffective for fat absorption, interferes with vitamin B12 absorption and might lead to nutrients malabsorption.
Several conditions related to a gastrointestinal disorder such as damaged mucosa, defects in the intestinal membrane transport system, impaired gastrointestinal motility, disrupted intestinal microbiota, or infections, these will either lead to impairment of absorption of all nutrients or specific nutrients.
GNE Gold-G® Health Food Series:
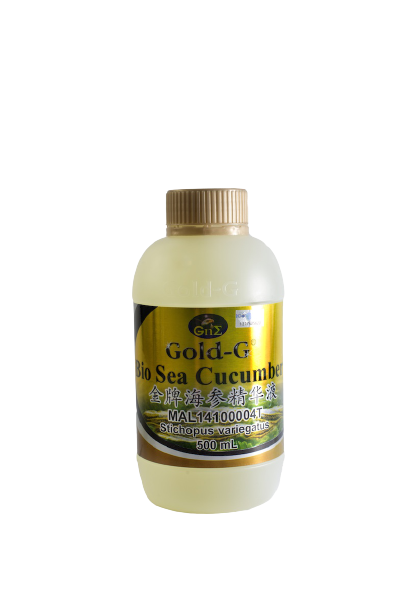
Gold-G® Bio Sea Cucumber
Sea cucumber is rich in pharmaceutical active components that provide beneficial effects on promoting gastrointestinal health, such as fucoidan, saponin, and polypeptides.
Fucoidan could reduce gastric ulcer, provide the anti-inflammatory and gastro-protective effect.
Saponin has high cytotoxic activity against cancer cells and helps to suppress tumor growth.
Polypeptides could help to alleviate oxidative damage and reduce inflammation in the body.
Precaution:
This product contains animal part: Sea Cucumber
Stop taking this product temporarily when you are experiencing a cough with phlegm, diarrhea and soft stool. Please consult your doctor or healthcare providers if you are taking blood-thinning medication or other medicines before consuming Gold-G Bio Sea Cucumber.
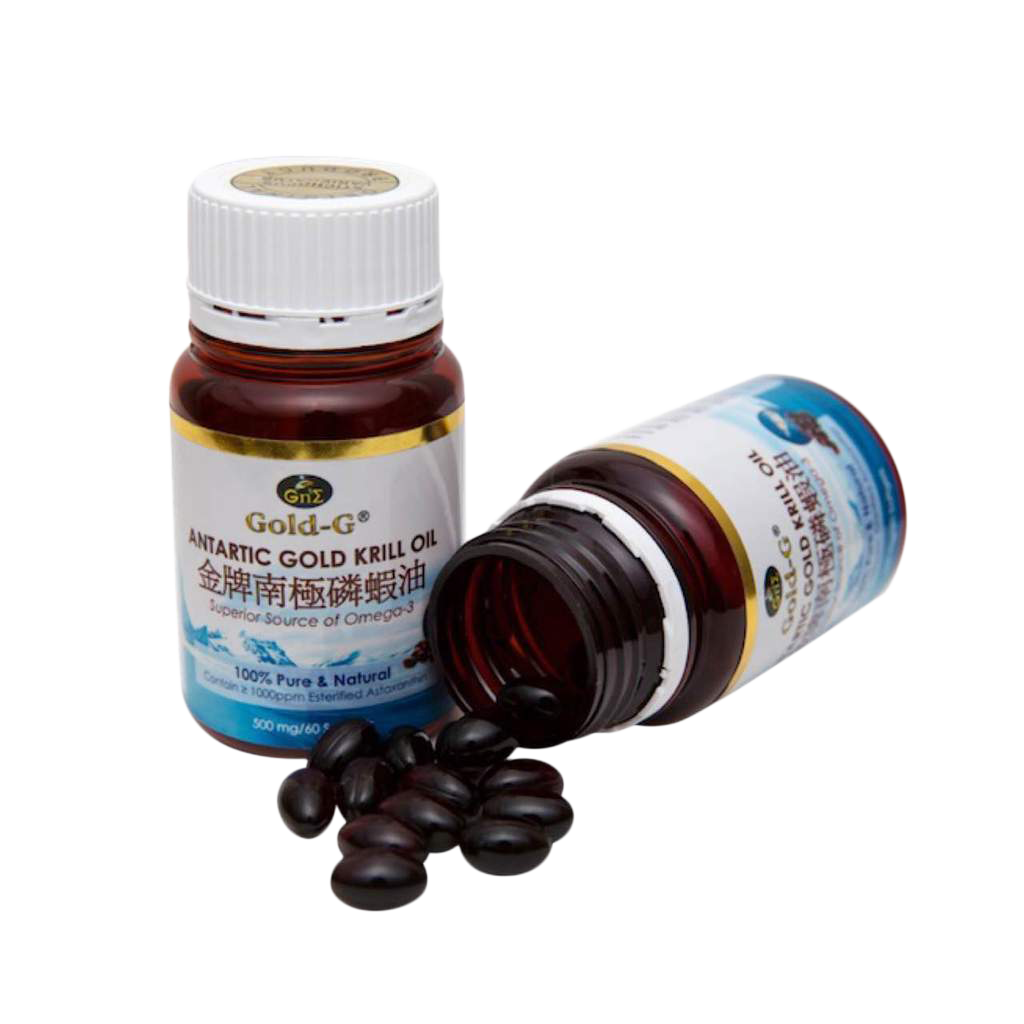
Gold-G® Antarctic Gold Krill Oil
Krill oil is an increasingly important source of omega-3 fatty acids specific for DHA and EPA. The fatty acids in krill oil are found in the form phospholipid, which provide better bioavailability in terms of absorption and effectiveness. Besides, krill oil also contained a natural antioxidant, astaxanthin that could protect against oxidation and provide several health benefits.
Omega-3 has an excellent anti-inflammatory property and provide protective effect against several inflammation diseases. It provides beneficial effects on reducing inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases and maintain healthy gastrointestinal system.
Astaxanthin is a strong antioxidant found in krill oil. It could help to decrease oxidative stress and scavenge the free radicals that cause damage on tissues and cells, reduce inflammation, and maintain gastrointestinal health.
Precaution:
Please consult your doctor or healthcare providers if you are taking blood-thinning medication or other medicines before consuming Gold-G Antartic Gold Krill Oil.
Gold-G® Gold Tualang Honey:
Tualang honey is raw honey harvested from Malaysia’s tropical rainforest. It is 100% pure and natural without undergo any additional treatment, hence it retained natural friendly bacteria, propolis, pollen grains, phytonutrients, phenolic acids, and flavonoids. Besides natural taste and aroma, Tualang honey has higher nutritional value and stronger therapeutic effects than processed honey!
Tualang honey possesses anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory effects, which could effectively reduce the risk of gastritis caused by infection and reduce inflammation on the stomach lining.
The prebiotic ingredients in raw honey such as inulin, oligosaccharide and oligofructose promote the growth of intestinal microbiota and aid in maintaining gastrointestinal health. Phenolic acids and flavonoids in Tualang honey could provide protection against oxidative damage.
Click the link below for direct purchase.
References
- Facts about moderate drinking. (CDC, 2019). Retrieved June 08, 2020, from https://www.cdc.gov/alcohol/fact-sheets/moderate-drinking.htm
- Hart, J. (n.d.). Stress. Retrieved June 08, 2020, from https://www.nutritionist-resource.org.uk/articles/stress.html
- Lopes, E. M., Carvalho, R. B., & Freitas, R. M. (2010). Analysis of possible food/nutrient and drug interactions in hospitalized patients. Einstein (São Paulo), 8(3), 298-302. doi:10.1590/s1679-45082010ao1672
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. (2000). Alcohol and Nutrition – Alcohol Alert No. 22- 1993. Retrieved June 08, 2020, from https://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/aa22.htm
- Shobha, (2019). Antibiotics and Nutritional Implications- The Drugs-Nutrients Interactions. Acta Scientific Nutritional Health, 3(6), 51-54. https://www.actascientific.com/ASNH/pdf/ASNH-03-0285.pdf
- Sulli, M. M., & Ezzo, D. C. (2017). Drug Interactions with Vitamins and Minerals. Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 1, 42-55. https://www.uspharmacist.com/article/drug-interactions-with-vitamins-and-minerals
- Tilburg, M. A. (2018). Stress Effects on the Body: Gastrointestinal System. Retrieved June 08, 2020, from https://www.apa.org/helpcenter/stress/effects-gastrointestinal
- Wolde, T. (2014). Effects of caffeine on health and nutrition: A Review. Food Science and Quality Management, 30, 59-65. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279923885_Effects_of_caffeine_on_health_and_nutrition_A_Review
- Zuvarox T, Belletieri C. Malabsorption Syndromes. (2020). Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553106/
- Park JM, Jeong M, Kim EH, Han YM, Kwon SH, Hahm KB. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Intake to Regulate Helicobacter pylori-Associated Gastric Diseases as Nonantimicrobial Dietary Approach. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:712363. doi:10.1155/2015/712363
- Drugs.com. (n.d.). Drug Interactions between Fish Oil and psyllium. https://www.drugs.com/drug-interactions/fish-oil-with-psyllium-1749-3873-1967-0.html
- Drugs.com. (2019). Antibiotics Guide. Available from: https://www.drugs.com/article/antibiotics.html
This website does not provide medical advice. The content of this website, such as graphics, images, text and all other materials, is provided for reference and educational purposes only. The content is not meant to be complete or exhaustive or to apply to any specific individual’s medical condition. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider regarding a medical condition.







